11. Pentecopterus
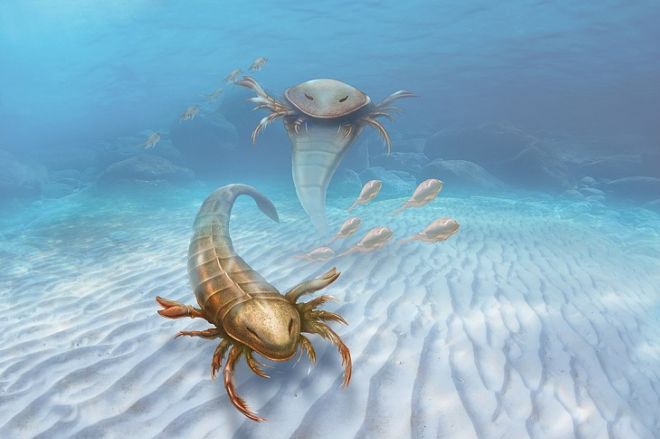

(By Patrick Lynch, Wikimedia Commons)
This artist’s rendering depicts a group of aquatic arthropods that existed around 460 million years ago. This sea scorpion would grow to a little under 6 feet in length, and its remains were first discovered in the city Deborah, Iowa.
12. Stethacanthus
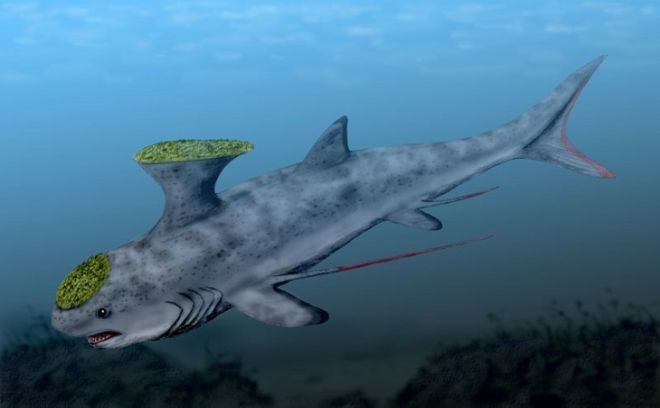

(By Nobu Tamura, Wikimedia Commons)
Though similar in appearance to sharks, this creature is, in fact, a Holocephalian, another subclass of cartilaginous fish, which became extinct approximately 320 million years ago. The fossils of this species have been discovered in Europe, Asia, and North America.
13. Woolly Rhinoceros
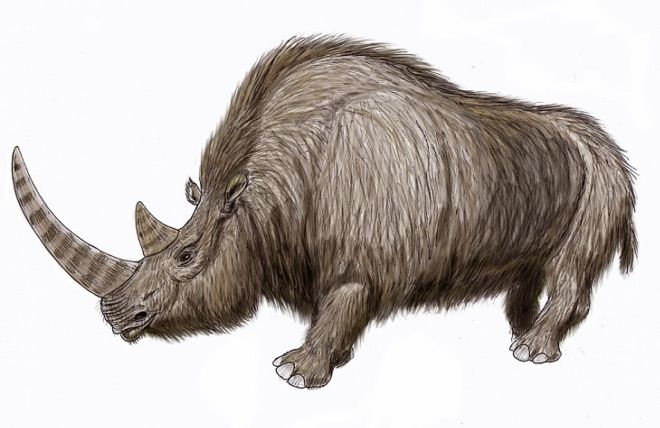

(By ?????, Wikimedia Commons)
Around the same time as the woolly mammoth roamed the Earth, the Woolly Rhinoceros was also making its way through Northern Asia and Europe. Woolly Rhinos survived until about 12,000 years ago. The oldest known fossil of this species was discovered in 2011 on the Tibetan Plateau.
14. Gastric-Brooding Frog
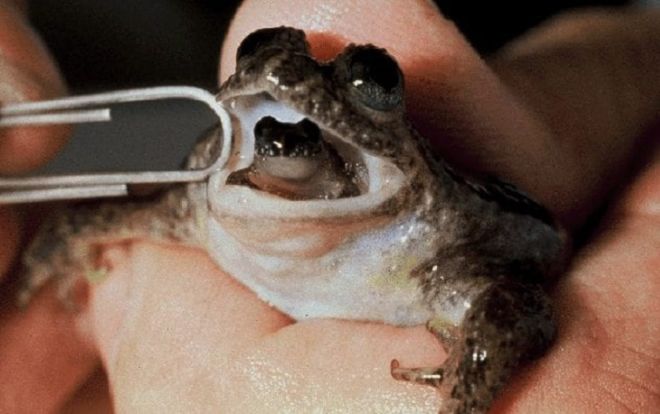

(global-greenhouse-warming.com)
The gastric-brooding frog is a unique species that incubates its young within its stomach and then regurgitates it once incubation is complete. This species died out relatively recently, the last official documented sighting of this animal was in 1983, in Queensland, Australia.
15. Jaekelopterus
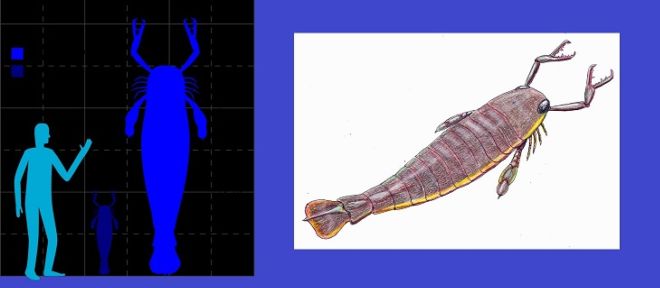
(By Slate Weasel, Wikimedia Commons) (Left), (By ?????, Wikimedia Commons) (Right)
Bearing a great resemblance to the Pentecopterus, the Jaekelopterus is a part of the predatory genus eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods that were found on the two ends of the planet, in Rhineland, Germany and Wyoming, US. They can grow to as large as 8.5 feet.
16. Short Faced Kangaroo
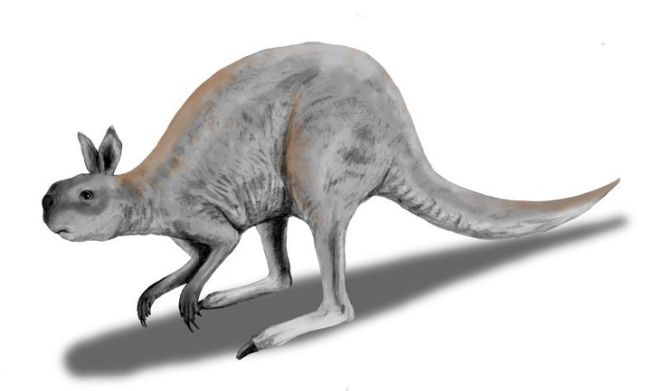
(By Nobu Tamura, Wikimedia Commons)
Also known as the procoptodon, the short-faced kangaroo was most commonly found in Australia. Under this genus is a species that is most notable for being the largest kangaroo ever known, growing up to 6.6 feet. It is believed to have gone extinct about 50,000 years ago, though evidence suggests some examples of the genus may have survived as recently as 18,000 years ago.
17. Tetropodophis amplecta
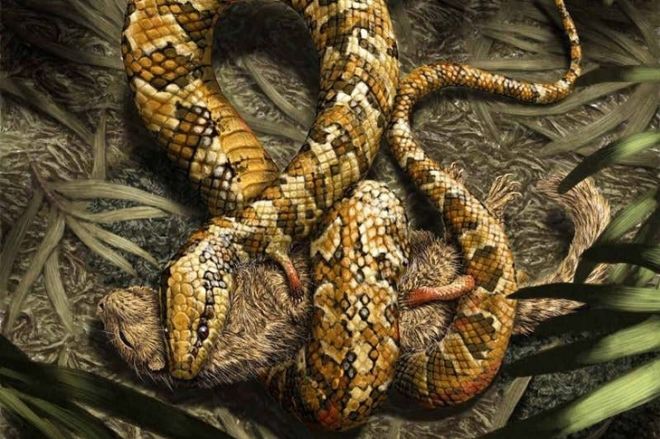

(Julius T. Cstonyi, newscientist.com)
This is an artist’s rendering of the Tetropodophis amplecta, also known as the four-legged snake. The fossil of this unique 120-million-year-old creature was unearthed in Brazil, and while this creature maintains all four legs of its ancestors, the legs were by no means used for transport and, aside from that, the animal maintains all the features of a typical snake.
18. Anomalocaris
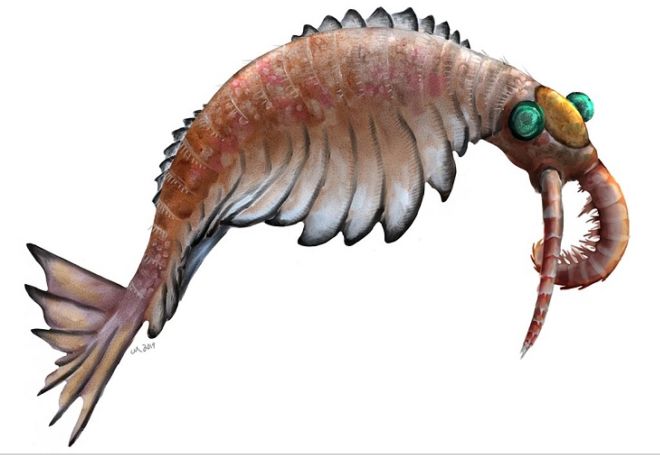

(By PaleoEquii, Wikimedia Commons)
This genus’ name literally translates to “unlike other shrimp”, or “abnormal shrimp”, and can be described as a hybrid of numerous aquatic species. The remains of this genus have been found in the fossil beds of Mt. Stephen and the Burgess Shale of the Canadian Rockies.
19. Platybeledon
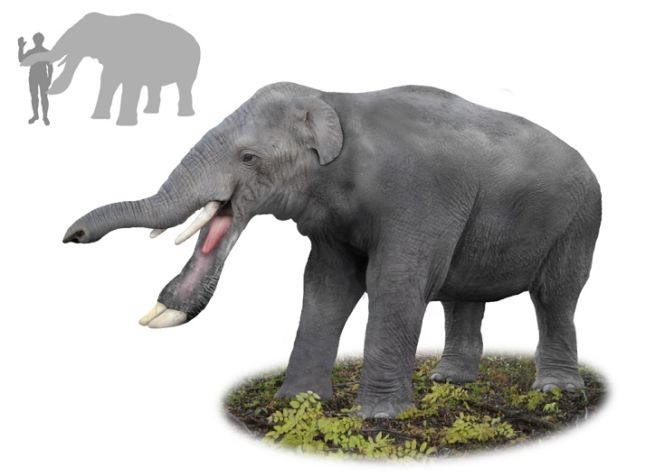

(By Tim Bertelink, Wikimedia Commons)
The species under this genus are massive herbivorous mammals closely related to the elephant family. The name of this genus translated to “flat-spear tusk”, which can be attributed to the strange appearance of the creature.
20. Golden Toad
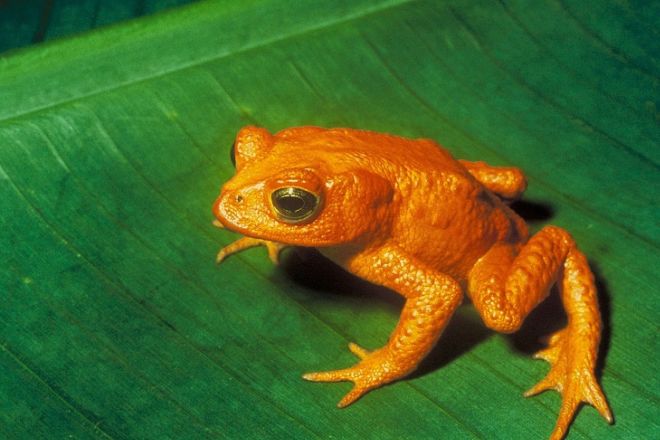

(By Bufo_periglenes1, Wikimedia Commons)
This toad, while not especially unusual in appearance apart from its bright hue, was first described in 1966 and last sighted in 1989. It is also called the Monte Verde toad, Alajuela toad, and orange toad and is considered the poster child of the decline in amphibian populations.






